Introduction
Grinding balls are essential components used in various industrial sectors for pulverizing materials into fine particles. They are widely employed in mining, cement plants, power stations, and chemical industries to grind materials such as minerals, cement, and chemicals into finer powders for further processing. Grinding balls play a crucial role in various industrial processes where size reduction of raw materials is required. From mining to cement production, these spheres are key in transforming coarse materials into finely ground powders, essential for manufacturing processes across industries. Understanding how grinding balls are manufactured sheds light on the precision and complexity involved in producing these vital components.
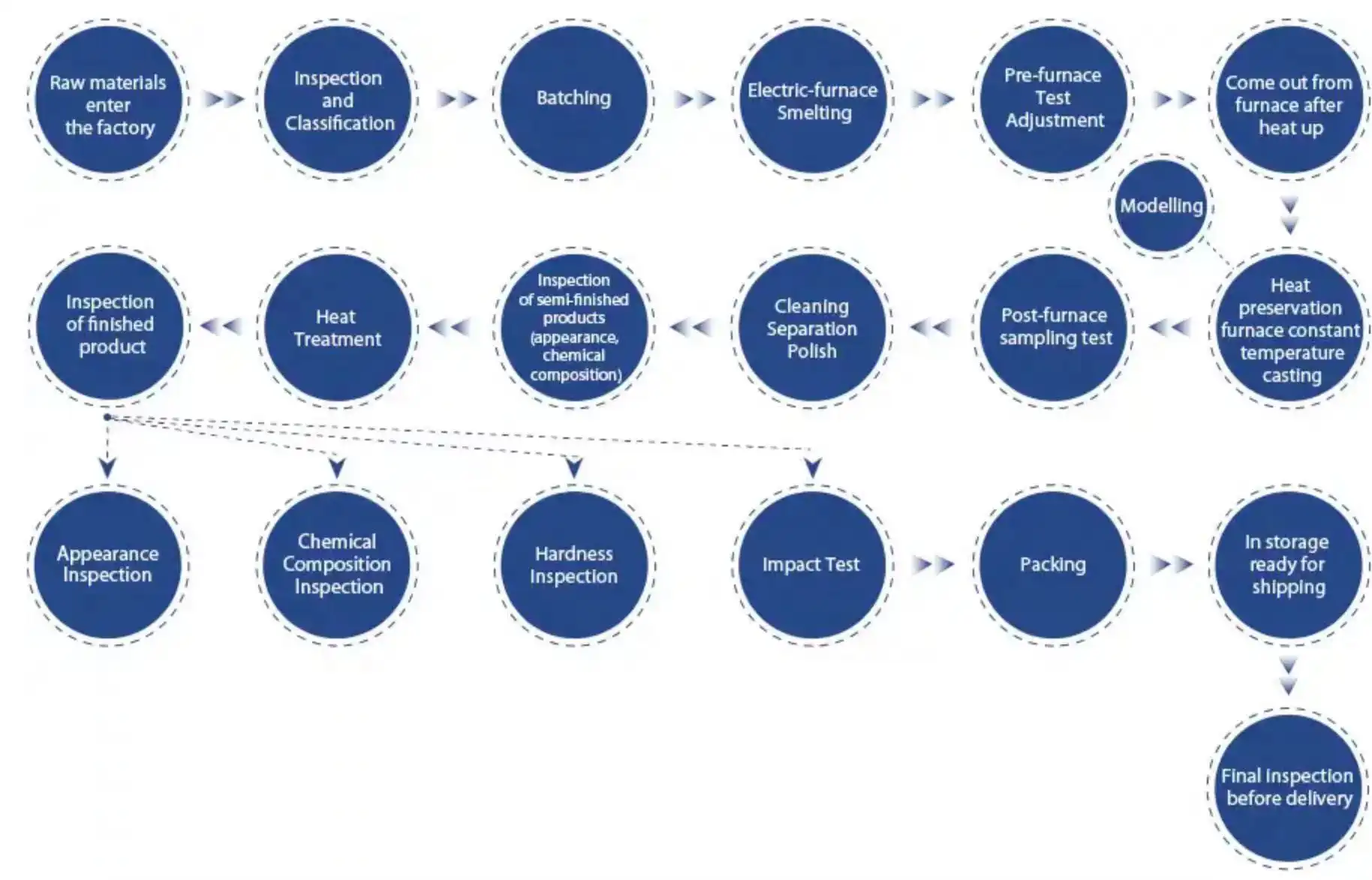
What materials are used to make grinding balls?
The manufacture of grinding balls begins with the inspection of raw materials. The primary materials used for production are typically steel and alloys, which are carefully selected based on their properties to withstand the wear and impact forces encountered in grinding applications. Carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel are commonly used due to their high hardness, toughness, and wear resistance properties.
Grinding balls are essential components in various industrial processes where size reduction of materials is required, such as in mining, cement production, and chemical engineering. The choice of materials for grinding balls depends on the application requirements, including hardness, wear resistance, impact resistance, and chemical compatibility with the material being ground. Here are the common materials used to make grinding balls:
Steel Balls:
Carbon Steel Balls: These are the most common type of grinding balls used due to their high hardness and wear resistance. Carbon steel balls are economical and suitable for general grinding applications.
Alloy Steel Balls: Alloyed with chromium (to enhance hardness and wear resistance) or other elements, alloy steel balls are used in specific milling environments where high abrasion resistance is required.
Ceramic Balls:
Alumina Balls: Made from high purity alumina, these balls offer high hardness, excellent wear and corrosion resistance, and good chemical stability. They are often used in ceramic, cement, paint, and chemical industries.
Zirconia Balls: Zirconia grinding media provide high strength, toughness, and excellent wear resistance. They are suitable for ultra-fine grinding applications and are chemically inert.
Stainless Steel Balls:
Stainless steel balls are resistant to corrosion and abrasion and find application in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and specialized chemical environments where contamination is a concern.
High Chrome Cast Iron Balls:
These balls are manufactured by casting process and are known for their high hardness (typically 58-65 HRC), excellent wear resistance, and good toughness. They are used in cement mills and in some mining applications.
Forged Steel Balls:
Forged grinding balls are made from steel bars that are heated and then forged into shape. They exhibit high hardness, good wear resistance, and are typically used in SAG (Semi-Autogenous Grinding) and ball mills for finer grinding.
Other Materials:
Ceramic-coated balls: These are steel balls with a ceramic coating to reduce wear and increase lifespan.
Glass balls: Used in agitator bead mills for grinding applications requiring high grinding efficiency and low contamination.
The choice of grinding ball material depends on factors such as the type of mill, operating conditions, and the material to be ground. Each material has its advantages and limitations, and selection is based on optimizing performance, cost-effectiveness, and durability for the specific application.
How are grinding balls shaped and formed?
The shaping of grinding balls is a critical step in their manufacturing process. Initially, molds in the shape of spherical segments are prepared, which will define the final shape and size of the grinding balls. These molds are typically made from sand or metal and are designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in the molding process.
The molten metal, after alloying and refining, is poured into these molds. The cooling process is carefully controlled to ensure uniform solidification and prevent defects such as cracks or uneven surfaces. Once cooled and solidified, the grinding balls undergo further processing to remove any excess material and refine their shape to precise tolerances.
Grinding balls may also undergo heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering to improve their mechanical properties. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the balls from elevated temperatures to increase hardness, while tempering reduces brittleness and internal stresses, enhancing toughness and durability.
What quality control measures are in place during grinding ball production?
Quality control is integral to grinding ball production to ensure consistent performance and longevity. Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent checks and tests are conducted at various stages:
Raw material inspection: Chemical composition analysis and physical property testing are performed to verify material quality before production.
Process control: Parameters such as temperature, cooling rates, and molding pressures are closely monitored and controlled to ensure consistency in ball properties.
Dimensional inspection: Finished grinding balls undergo precise measurement to verify diameter, roundness, and surface smoothness, ensuring they meet specified tolerances.
Hardness testing: Rockwell or Brinell hardness tests are conducted to assess the hardness of the balls, which directly impacts their wear resistance and performance in grinding applications.
Impact and wear testing: Balls are subjected to impact tests to evaluate their resistance to fracturing under high-stress conditions. Wear tests simulate grinding conditions to assess the balls' durability over extended periods.
Quality assurance: Sampling and batch testing are conducted according to international standards such as ISO and ASTM to ensure compliance with performance specifications.
By adhering to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can guarantee that grinding balls meet the demands of diverse industrial applications, providing reliable performance and efficiency in grinding operations.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of grinding balls is a complex blend of metallurgy, mechanical engineering, and quality control. From selecting raw materials to the final inspection of finished products, every step is crucial in ensuring the reliability and performance of these indispensable components. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality grinding balls remains paramount, driving ongoing advancements in manufacturing technologies and quality standards.
References
1. "Manufacturing Processes for Grinding Balls: A Review," International Journal of Powder Metallurgy, 2018.
2. "The Production and Properties of Grinding Balls," Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019.
3. "Advanced Techniques in Grinding Ball Manufacturing," Materials Science and Engineering, 2020.
4. "Grinding Ball Fabrication: Techniques and Technologies," Powder Technology, 2021.
5. "Innovations in the Production of Grinding Media Balls," Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022.
6. "Overview of Grinding Ball Manufacturing Methods," Wear, Elsevier, 2017.
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)








